EU Referendum survey results: UK will very likely remain in EU and sterling may appreciate
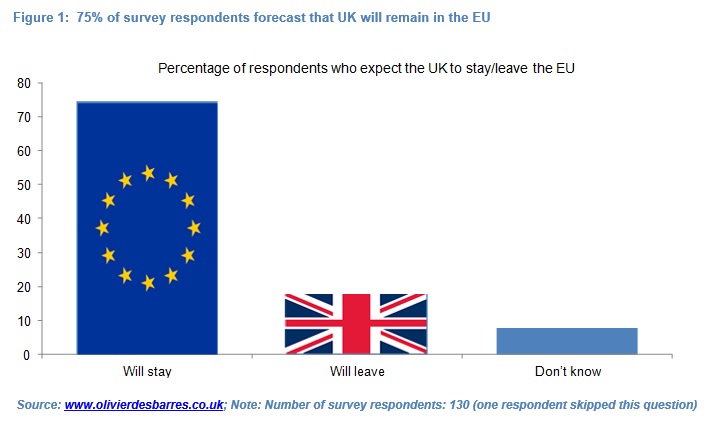
75% of 130 analysts, consultants, journalists, finance specialists, real-sector heads, policy-makers and portfolio managers forecast that the UK electorate will vote in favour of the UK remaining in the European Union (EU) in the 23rd June referendum, in a survey which I conducted between the 10th and 16th May. That ratio jumps to 81% when the 10 respondents who did not have a view are excluded.
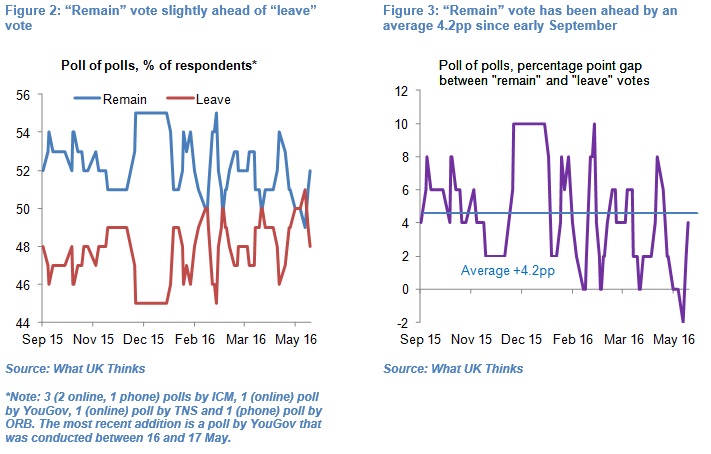
By comparison, the latest poll-of-polls conducted by What UK Thinks has the “remain” vote on 52% and “leave” vote on 48% five weeks before this crucial vote. But caution is warranted given the large share of undecided voters, the importance of turnout and differing results depending on whether polls are by phone or on-line. Current prices offered by betting companies suggest a comfortable victory for the “remain” vote.
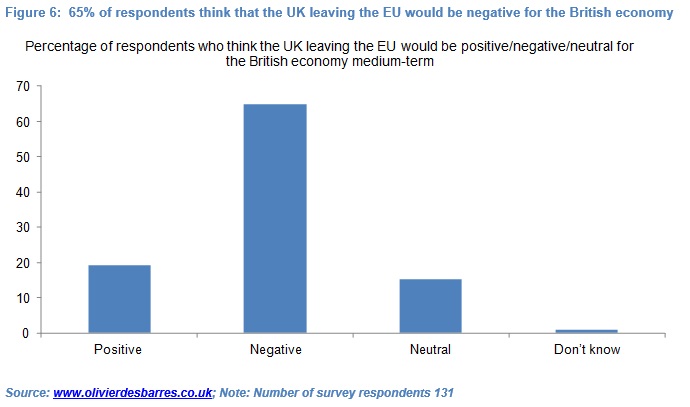
Of the 130 respondents with a view which I surveyed, 65% forecast that the UK leaving the EU would be negative for the British economy medium-term. 19% forecast that it would be positive and 15% that it would be neutral[1]. This is broadly in line with the view expressed by Prime Minister Cameron and “remain” camp, the Bank of England and IMF.
The risk to the currency is forecast to be somewhat asymmetric. There is an overwhelming view amongst those surveyed that, if the UK leaves the EU, sterling will depreciate while 38% forecast sterling to depreciate or remain stable should the UK remain in the EU.
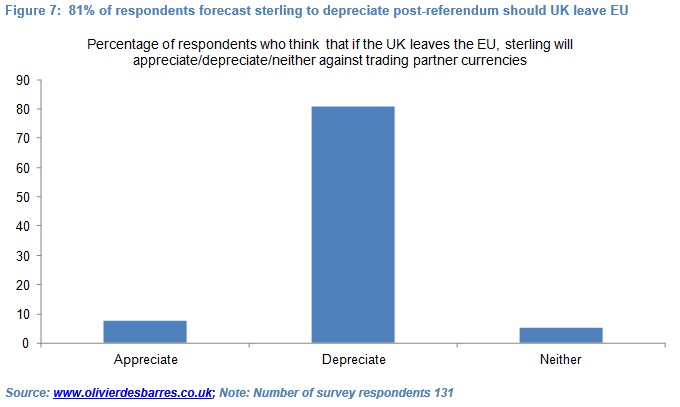
Specifically, out of 131 respondents, 81% forecast that if the electorate votes for the UK to leave the EU, sterling would depreciate between the referendum and end-year against the currencies of the UK’s key competitors. Only 8% forecast that sterling would appreciate, while 6% thought that the currency would be broadly stable. 6% did not express a view.
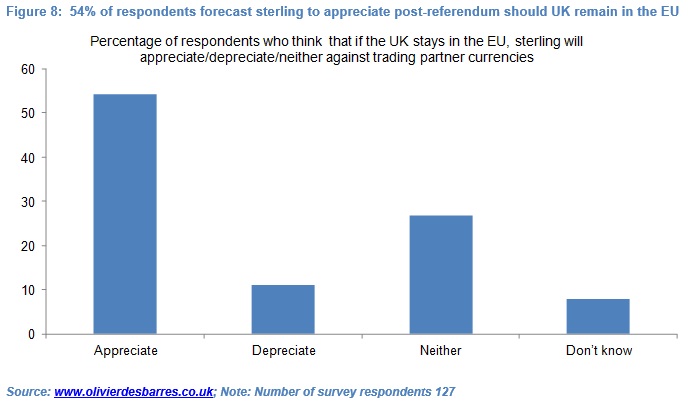
But out of 127 respondents, only 54% forecast that if the UK remains in the EU sterling would appreciate. 11% forecast that sterling would depreciate, while 27% thought the currency would be broadly stable. 8% did not express a view.
These survey results tend to back my view, expressed in What to expect in 2016 – same, same but worse, that the electorate will vote for the UK to remain in the EU and that the lifting of this uncertainty will see a reasonably competitive sterling appreciate.
But any currency rally is likely to be moderate given the UK’s structural deficiencies, including a large current account deficit, low productivity and weak wage growth, and a dovish central bank. A “remain” vote will not address these vulnerabilities near-term.
Finally, a note of caution. Like all polls, this survey may contain unintended biases which are difficult to ascertain let alone measure accurately.
The survey consisted of four sets of questions and was open from 10th May 2016 (12:00) to 16th May 2016 (12:00). Respondents could chose to skip one or more questions. I would like to thank the 131 analysts, consultants, journalists, finance specialists, real-sector heads, policy-makers, portfolio managers, sell-side salespeople, strategists and traders who responded to this survey.
Broad consensus forecast that UK will remain in the EU
Question 1: How do you expect the UK electorate to vote in the 23rd June 2016 referendum on EU membership?
75% of the 130 respondents surveyed forecast that the UK electorate will vote in favour of the UK remaining in the European Union in the 23rd June referendum (see Figure 1). That ratio jumps to 81% when the 10 respondents who did not have a view are excluded.
Popular opinion polls have “remain” marginally ahead of “leave” but many caveats
By comparison, the latest poll-of-polls conducted by What UK Thinks, which averages the results of the last six phone and on-line opinion polls, has the “remain” vote on 52% and “leave” vote on 48% (Figure 2)[2]. The “leave” vote has only been ahead of the “remain” vote once since September and has on averaged trailed the “remain” vote by about 4.2 percentage points (see Figure 3).
But caution is warranted, due amongst other factors to i) the large share of undecided voters, ii) the importance of turnout, and iii) the difference in results between online and phone surveys.
The Daily Telegraph estimates that in the 100 EU referendum polls conducted since early September, undecided voters accounted on average for 15%. While assumptions can be made about how they will ultimately vote on referendum day, these undecided voters could swing the outcome either way.
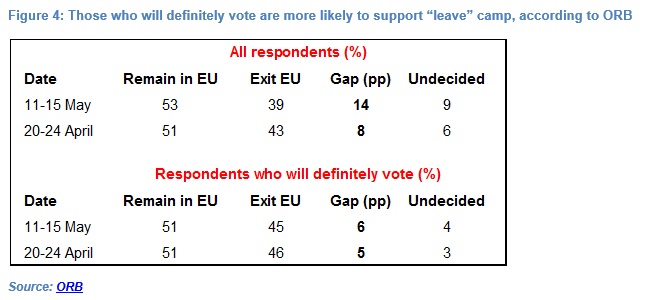
Moreover, turnout may influence the referendum’s outcome with those who support the “leave” camp more likely to definitely vote according to ORB. In its last poll conducted on 11-15th May, ORB found that 53% of respondents would vote “remain” – an increase of 2 percentage points from a poll conducted on 20-24th April – and 39% backed “leave” – a 4 percentage point decrease. But this large gap shrinks considerably if we take into account that 53% of “remain” voters and 62% of “leave” voters said they would definitely vote. If only those voters are included, support for “remain” falls to 51% while support for “leave” rises to 45% (see Figure 4).
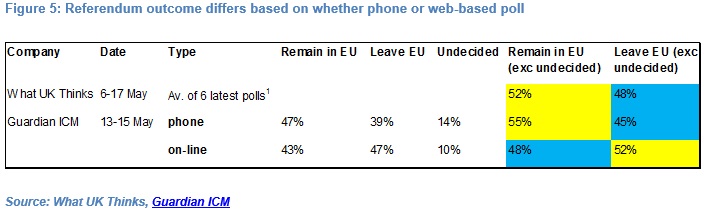
Finally, since the start of September, phone polls suggest an average 17 percentage point lead for “remain” while online polls have it at just 2 percentage points according to the Daily Telegraph[3]. In the latest ICM poll conducted on 13-15th May, the phone poll had the “remain” vote comfortably ahead of the “leave” vote but the online poll had the “leave” vote slightly ahead (see Figure 5).
Betting companies’ pricing points to comfortable “remain” victory
The inherent limitations of opinion polls were made evident in the 2015 general elections, with none of the polls predicting the incumbent Conservative Party’s comfortable victory. As a result there has been increasing focus on betting companies’ odds of a “remain” or “leave” victory.
After all, while those polled may have a reason not to declare their true voting intentions, they are more likely to put their money where their mouths are when real financial gains (or losses) are at stake. Prices offered by the main UK bookmakers point to a clear “remain” victory, with odds of 1/4 for the UK to remain in the EU and 11/4 for the UK to leave the EU.
My core scenario remains a victory for “remain” vote
Any forecast of the referendum outcome remains tentative but I maintain my core scenario expressed in What to expect in 2016 – same, same but worse (19 January 2016) that Prime Minister Cameron will secure a “remain” vote, premised on:
- The greater domestic support for the “remain” vote from the political and business sphere as well as international community, which will count when campaigning really intensifies in coming weeks.
- The UK’s electorate’s conservative nature. The “yes” vote in Scotland’s 2014 referendum on UK membership suggests that the collective desire to be part of a union should not be under-estimated, while the incumbent Conservative Party’s convincing win in the May 2015 elections underlines the electorate’s affinity for continuity, rather than the unknown.
Two-thirds of respondents think UK leaving EU would be negative for British economy
Question 2: If the UK electorates votes in favour of the UK leaving the EU, do you think this will be positive, negative or neutral for the British economy medium-term?
65% of the 131 respondents forecast that the UK leaving the EU would be negative for the British economy medium-term. 19% forecast that it would be positive and 15% that it would be neutral. One respondent did not have a view (see Figure 6). This is broadly in line with the assessment presented by Prime Minister Cameron, Chancellor Osborne and the “remain” camp, as well as the Bank of England and International Monetary Fund.
In its latest quarterly inflation report, the Bank of England concluded that “a vote to leave the EU could have material economic effects – on the exchange rate, on demand and on the economy’s supply potential […]. Aggregate demand would also likely fall, relative to our forecast, in the face of tighter financial conditions, lower asset prices, and greater uncertainty about the UK’s trading relationships. Households could defer consumption, and firms could delay investment. Global financial conditions could also tighten, generating potential negative spillovers to foreign activity that, in turn, could dampen demand for UK”.
The IMF, in its latest Article IV Consultation, concluded that if the UK remained in the EU GDP growth would rebound in H2 2016. Conversely, the UK leaving the EU would:
- Lead to a protracted period of heightened uncertainty and financial market volatility;
- Substantially depress UK productivity, trade, output, incomes, consumption, investment and fiscal revenues;
- Potentially weaken UK equity and house prices; and
- Potentially increase UK borrowing costs for households and businesses and inflation.
Respondents forecast asymmetric sterling reaction-function
Question 3: If the UK electorate votes in favour of the UK leaving the EU, how do you expect sterling to perform between the referendum and end-year against the currencies of the UK’s key competitors?
Out of 131 respondents, 81% forecast that if the electorate votes for the UK to leave the EU, sterling would depreciate between the referendum and end-year against the currencies of the UK’s key competitors (see Figure 7). Only 8% forecast that sterling would appreciate, while 6% thought that the currency would be broadly stable. 6% did not express a view. If the 8 respondents who did not have a view are excluded, the percentage of respondents expecting sterling to depreciate rises to 86%.
Question 4: If the UK electorate votes in favour of the UK remaining in the EU, how do you expect sterling to perform between the referendum and end-year against the currencies of the UK’s key competitors?
Out of 127 respondents, only 54% forecast that if the UK remains in the EU sterling would appreciate (see Figure 8). 11% forecast that sterling would depreciate, while 27% thought the currency would be broadly stable. 8% did not express a view. If the 10 respondents who did not have a view are excluded, the percentage of respondents expecting sterling to appreciate rises to 59%.
Sterling likely to appreciate post referendum if UK votes to remain in EU
These survey results tend to back my view, expressed in What to expect in 2016 – same, same but worse, that the electorate will vote for the UK to remain in the EU and that the lifting of this uncertainty will see a reasonably competitive sterling appreciate.
There has been mounting evidence that domestic and foreign companies have curtailed or delayed investment in the UK, with domestic companies also prone to freezing hiring a as a direct result of the uncertainty associated with the referendum outcome. In UK referendum on EU membership – darkness before dawn (26 February 2016), I highlighted eight layers of uncertainty: 1. How the electorate will vote; 2. The (un)reliability of opinion polls; 3. The lack of political unity; 4. The lack of precedent; 5. The lack of explicit contingency plans; 6. Prime Minister Cameron’s future; 7. The possibility of another Scottish referendum; and 8. The possibility of a second EU referendum if the result on 23rd June is too close to call.
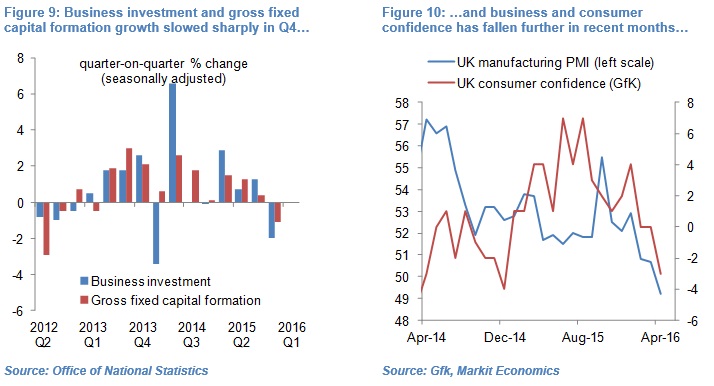
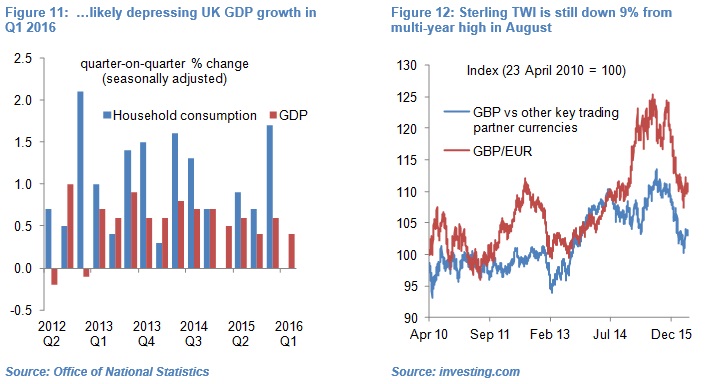
UK gross fixed capital formation, seasonally-adjusted, contracted 1.1% quarter-on-quarter in Q4 2015 – the largest contraction in over three years (see Figure 9). Similarly, business investment shrunk 2% qoq in Q4 2015 – the second largest quarterly contraction in seven years – which wiped out the growth in the previous two quarters. Delayed or curtailed investment has in all likelihood contributed to business and consumer confidence falling to multi-month lows (see Figure 10), which in turn depressed consumer spending, investment and GDP growth in Q1 2016[4] (see Figure 11).
A “remain” victory on 23rd June would remove this uncertainty with a return to the norm and likely unlock delayed or curtailed investments in capital and labour. In the event of a “leave” victory, there would still be a great deal of uncertainty near-term as ultimately there is no precedent for a country leaving the EU and thus no clear-cut rulebook to rely on.
Moreover, the British economy is likely to benefit at the margin from the lagged impact of a more competitive currency even if weak global demand is likely to dull any narrowing of the UK trade deficit. Sterling’s trade weighted index (TWI) has recovered slightly in the past few weeks, but is still down 9% from its seven-and-a-half-year high recorded nine months ago according to my estimates (see Figure 12).
Finally, sterling’s depreciation should, all other things being equal, have an inflationary impact (as the sterling-cost of imports rises). This may be sufficient for the Bank of England to communicate a less dovish, if not more hawkish, policy stance even if core inflation, which has been running at 1.2-1.5% year-on-year, is unlikely to become an issue in the near-term.
Post-referendum rally likely blunted by underlying UK imbalances and dovish central bank
However, any currency rally is likely to be moderate until the government addresses structural deficiencies, including a large current account deficit, low productivity, still-high levels of household debt and fiscal deficits and weak wage growth, and the Bank of England turns more hawkish. The fact that survey respondents are less confident about sterling appreciating in a “remain” scenario than they are about sterling depreciating in a “leave” scenario may indeed be due to these underlying weaknesses which a “remain” vote will not fully address.
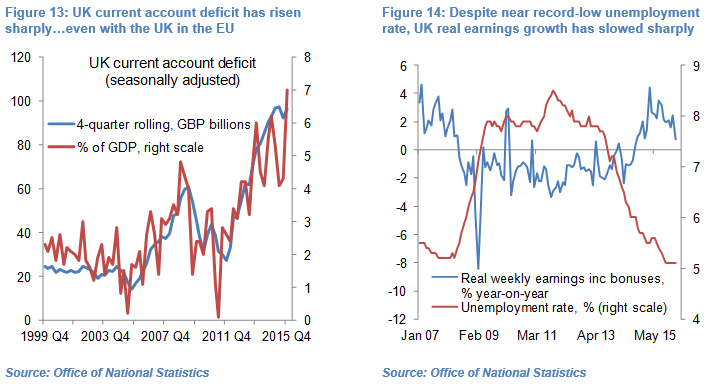
Specifically, the UK is running a record-high current account deficit (see Figure 13), as a result of a widening of the goods and services trade deficit, a decrease in receipts from direct investment and portfolio investment abroad and an increase in payments to foreign direct investors.
At the same time the Bank of England is showing no sign of wanting to hike its record-low policy rate of 0.5%, in the face of tepid wage and consumer price inflation. While the UK unemployment rate has been stable near a record-low of 5.1% since October, growth in real earnings (including bonuses) has slowed sharply in recent months, suggesting there is still a fair degree of slack in the UK labour market (see Figure 14). This is likely contributing to modest core-inflation which fell to 1.2% year-on-year in April and remains steady around its 2-year average.
Olivier Desbarres
Olivier Desbarres currently works as an independent commentator on G10 and Emerging Markets. He has over 15 years’ experience with two of the world’s largest investment banks as an emerging markets economist, rates and currency strategist.
[1] Total may not add up to 100% due to rounding
[2] The question posed is the one approved by the Electoral Commission for the actual referendum: “Should the United Kingdom remain a member of the European Union or leave the European Union?”
[3] As there have been three times as many online polls as phone polls, the weighted average of the difference between the “remain” and “leave” votes is skewered towards the online poll results.
[4] A breakdown of Q1 2016 GDP is due for release on 26th May